Sarmiza Elena Stanca
Leibniz Institute of Photonic Technology, Germany
Title: Secure accuracy at increase precision of AFM-probe integrated biosensor
Biography
Biography: Sarmiza Elena Stanca
Abstract
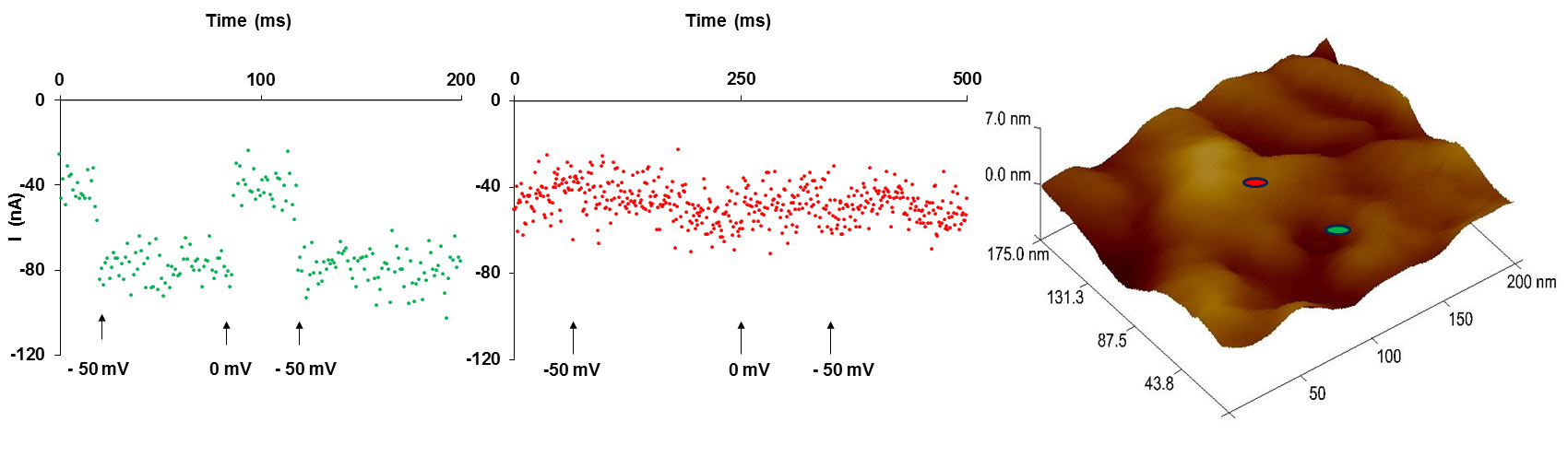
The plasma membrane regulates the selective interchange of matter between the interior and the exterior of the cell. Understanding this complex process requires knowledge of the plasma membrane´s molecular constituents. Topical reports prove the access to the molecular level of the synthetic membrane by atomic force microscopy (AFM). This technique also permits an electrochemical investigation in the immediate vicinity of the tip. An electrochemical and topographic study of the living cell membrane, by the mean of an AFM-probe integrated amperometric biosensors is employed to localize specific molecules in the natural cellular membrane (Figure 1). Several materials and shapes of the AFM probes integrated in different systems are presented. It is underlined that the selection of control experiment is decisive in achieving accurate findings. The central concern of this study is how to preserve the sensor response accuracy while increasing its precision.
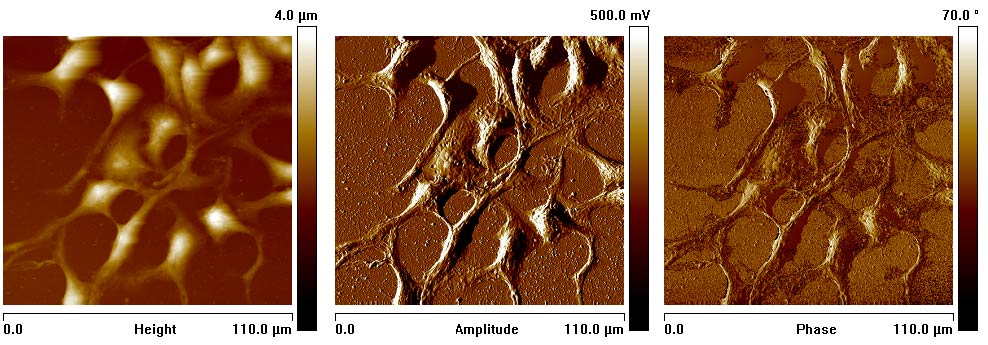
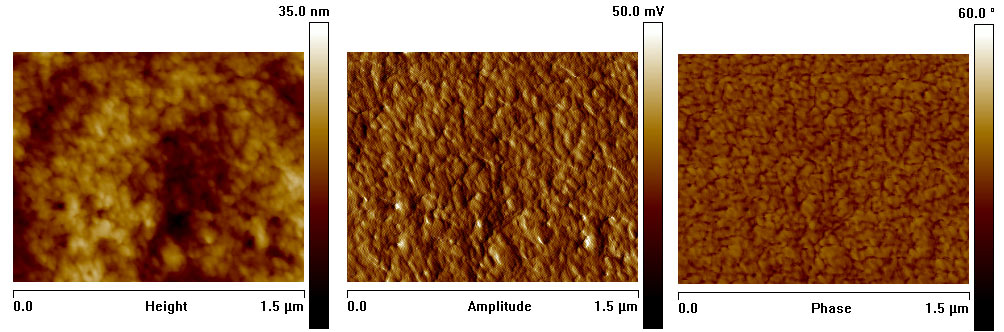
Figure 1: (A) Height, amplitude and phase atomic force micrographs (110 µm x 110 µm) of the cells immobilized on conductive glass; (B) Height, amplitude and phase AFMs in one location of 1.5 µm x 1.5 µm of the plasma membrane; (C) AFM probe integrated sensor signal on two different points: green and red marked on the AFM image (200 nm x 200 nm).
A)
B)
C)